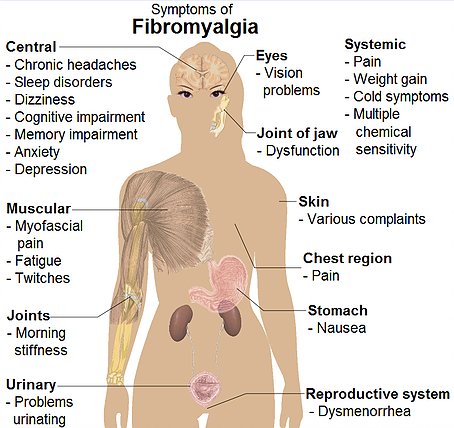
WHAT IS FIBROMYALGIA?
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is characterised by pain or tenderness in multiple muscle groups throughout the body. This widespread pain pattern is often accompanied by other symptoms including muscle stiffness, fatigue, headaches, irritable bowel syndrome, and problems with concentrating (sometimes called ‘fibro-fog’). It’s estimated to affect up to 1 in 20 people, and is 7 times as likely to affect women. Onset is typically in the 30 to 50 age range.
HOW IS FIBROMYALGIA DIAGNOSED?
There is no specific test to confirm fibromyalgia. Diagnosis is usually made using the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 1990 Criteria:
This is:
Widespread pain for more than 3 months duration
Tenderness reported on manual pressure on 11 or more out of 18 specific points across the body
New diagnostic guidelines were introduced in the ACR 2010 guidelines, which included factors such as quality of sleep, levels of fatigue and cognitive function.
WHAT CAUSES FIBROMYALGIA?
FMS is often associated with rheumatic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. There is increasing interest in the interaction of role of gut bacteria, stress and inflammation on the body’s immune response in these conditions. Onset is usually related to a stressful life event such as bereavement or a relationship breakdown, or a physical trauma including falls, infections, giving birth, and operations.
FMS suffers exhibit an altered chemical balance of signaling hormones such as serotonin, noradrenaline, dopamine and cortisol, which may alter pain processing in the brain. Recent research has also pinpointed clear anatomical changes that can be seen in sufferers, including an increased sensory innervation to structures in the hand called arterio-venous shunts.
WHAT TREATMENTS ARE AVAILABLE FOR FIBROMYALGIA?
Medications
Prescribed drugs focus on providing symptomatic relief, and may include antidepressants such as TCAs and SSRIs, in addition to painkillers including codeine and tramadol.
Manual therapy
Osteopathy is a gentle manual therapy, which is effective for treating fibromyalgia. Treatment is focused on reducing pain and stiffness in muscles and improving the overall mobility of the body. Specific techniques to improve the lymphatic flow (the ‘waste clearance’ system of the body) may also be used. Patients often report an improvement in sleep following treatment.
Diet
There are no good studies investigating diets role in FMS, but anecdotally, avoiding certain food groups works for many sufferers. Foods which may play a role in worsening symptoms include:
additives such as MSG and nitrates (found in many processed foods),
sugar, fructose, aspartame (an artificial sweetener), sweet fizzy drinks
caffeine and chocolate
yeast and gluten
dairy
tomatoes, potatoes and peppers
Exercise
Exercise has been shown to be effective for reducing the pain associated with fibromyalgia. 30 minutes of daily exercise, such as walking, swimming or yoga, is beneficial for your general health, helping to reduce stress levels, improve lymphatic flow and lower blood pressure. As people with FMS experience widespread pain in muscles, they tend to become less active, so a gentle return to exercise is important.
Talking Therapies
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) or other talking therapies such as counselling or hypnotherapy may be useful to reduce stress levels in FMS sufferers.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Marianne Carpenter is an osteopath and clinical anatomist. She works in private practice in Bath treating a wide range of patients, and teaches anatomy at Swansea Medical School.